Understanding LPG and CNG vehicles(1)
Switching from oil to gas: Understanding LPG and CNG vehicles
LPG and CNG are two mainstream alternatives for vehicle fuel. With the development of environmental awareness and the automotive industry, their applications are becoming more and more widespread.
1. Definition and advantages of LPG and CNG
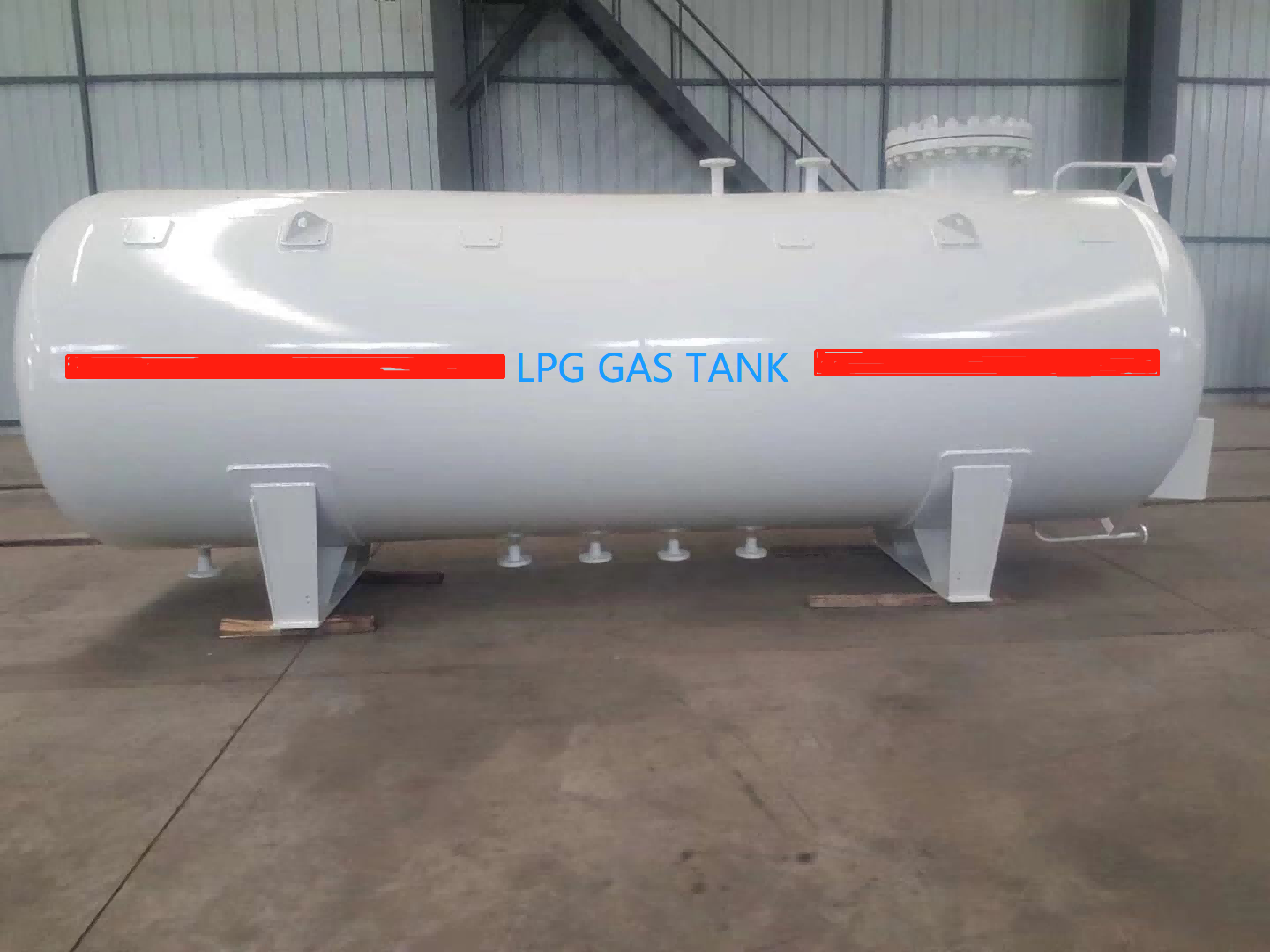
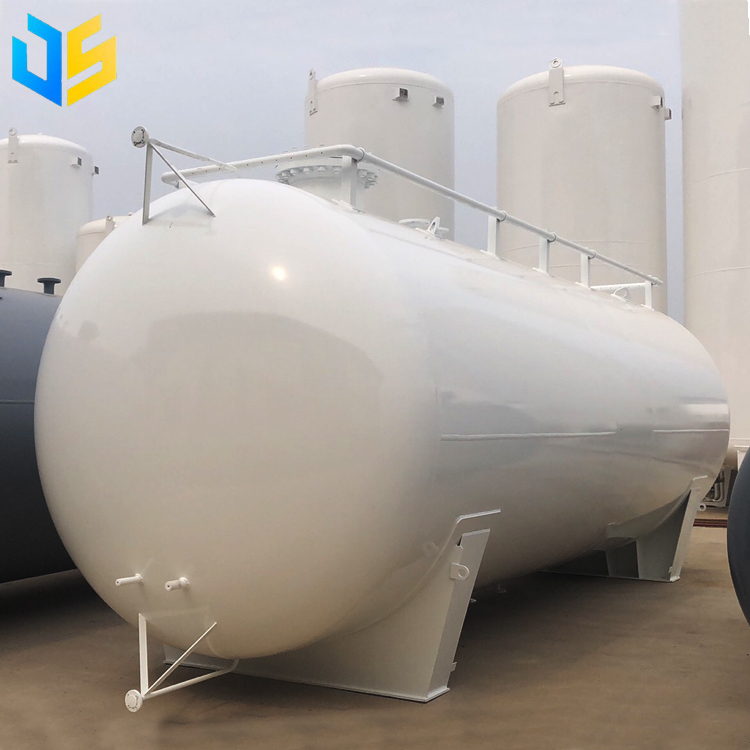
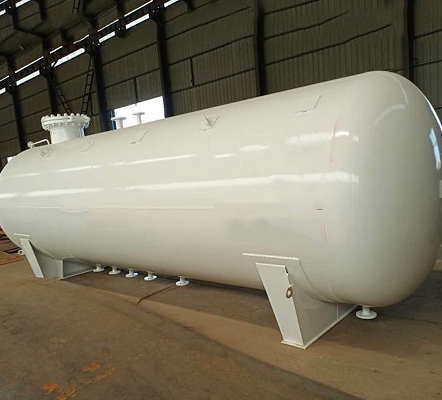
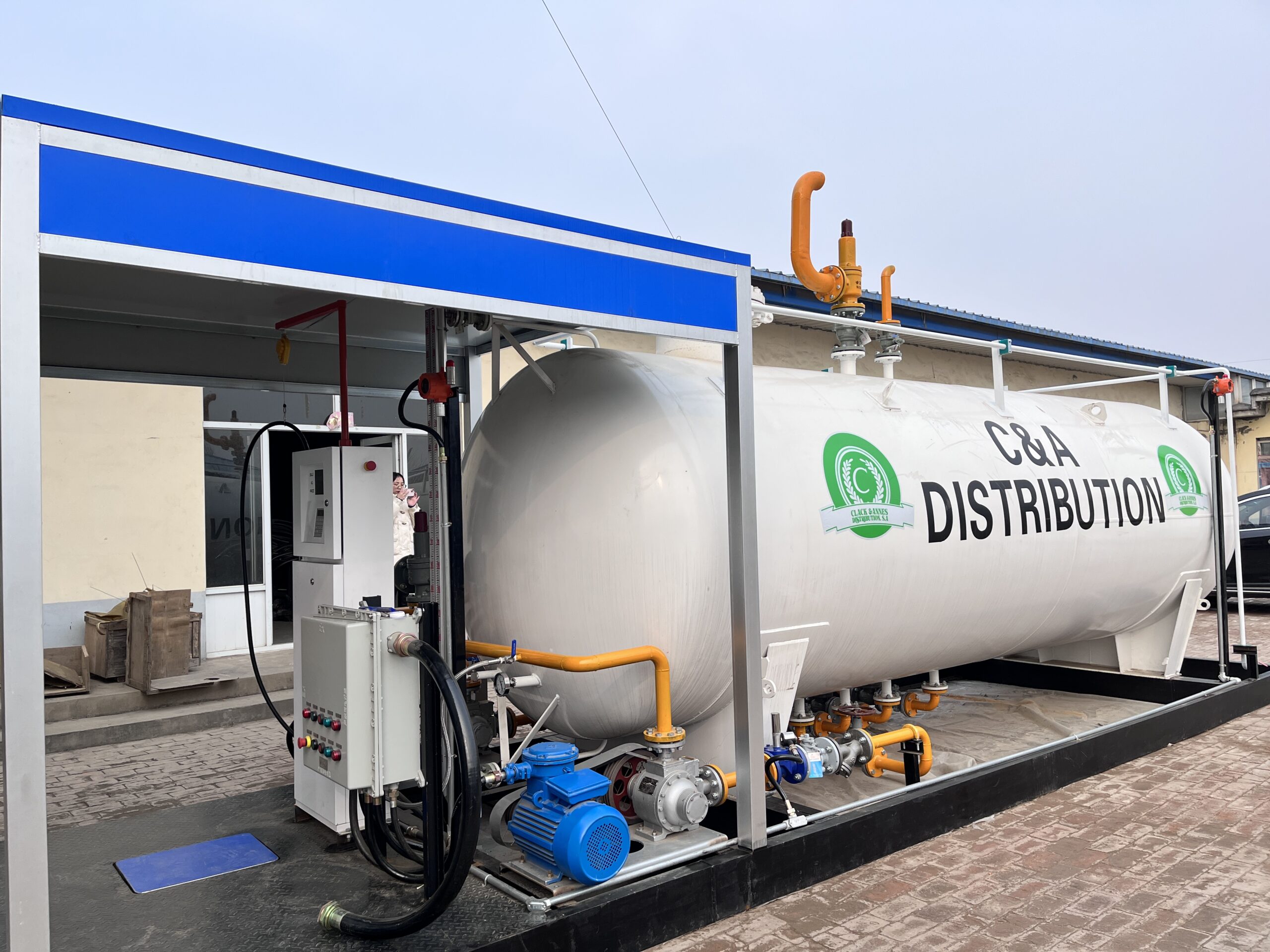
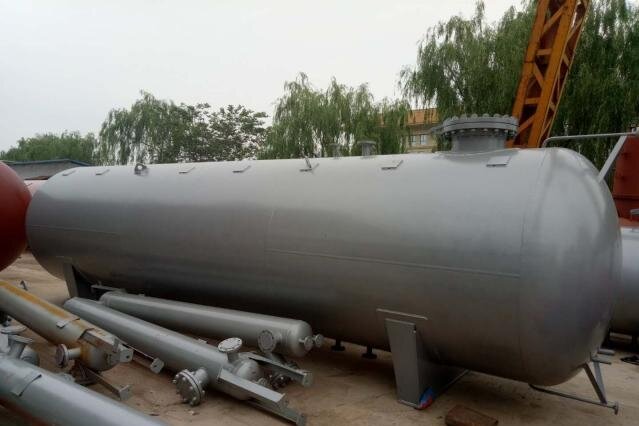
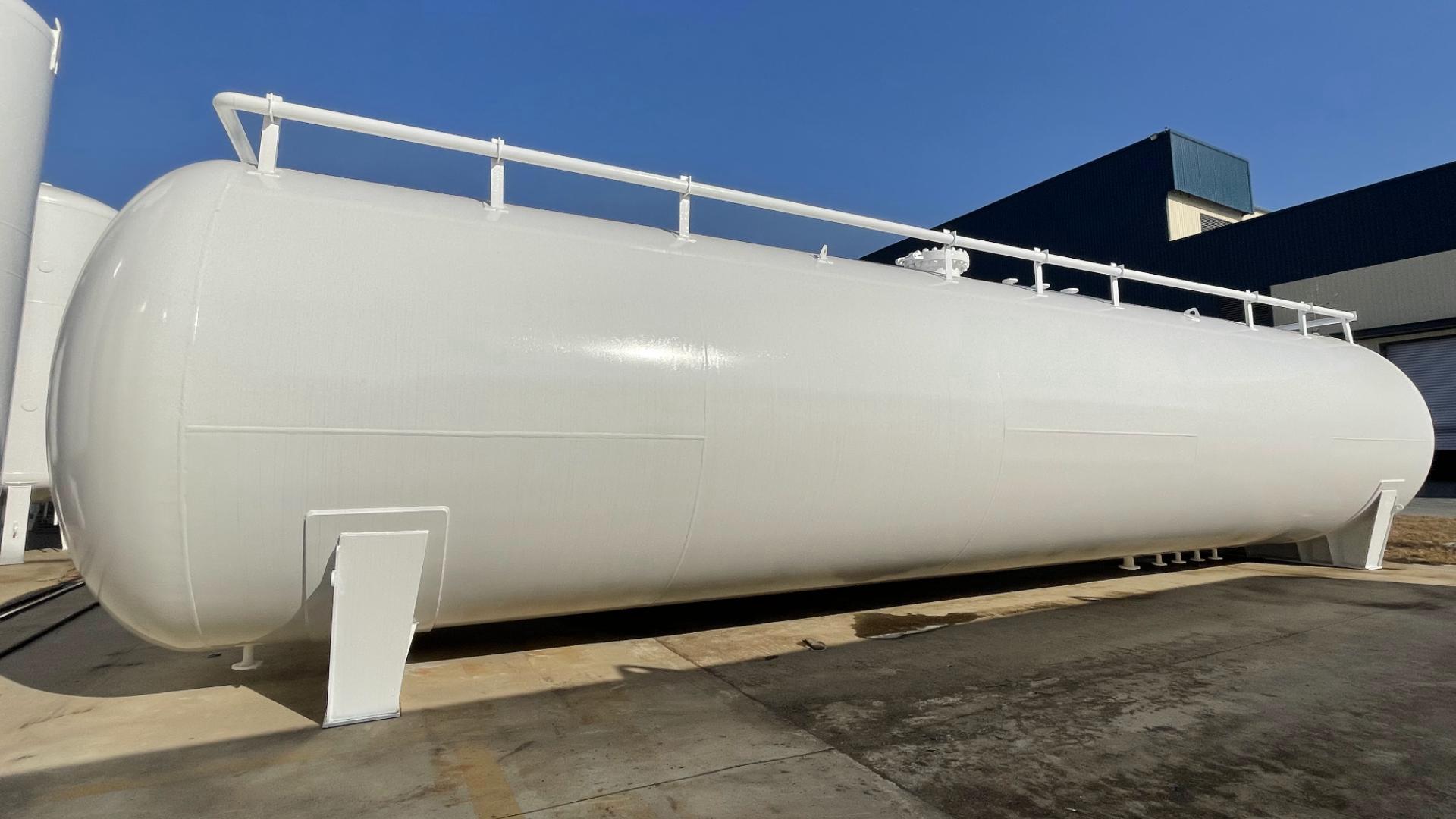
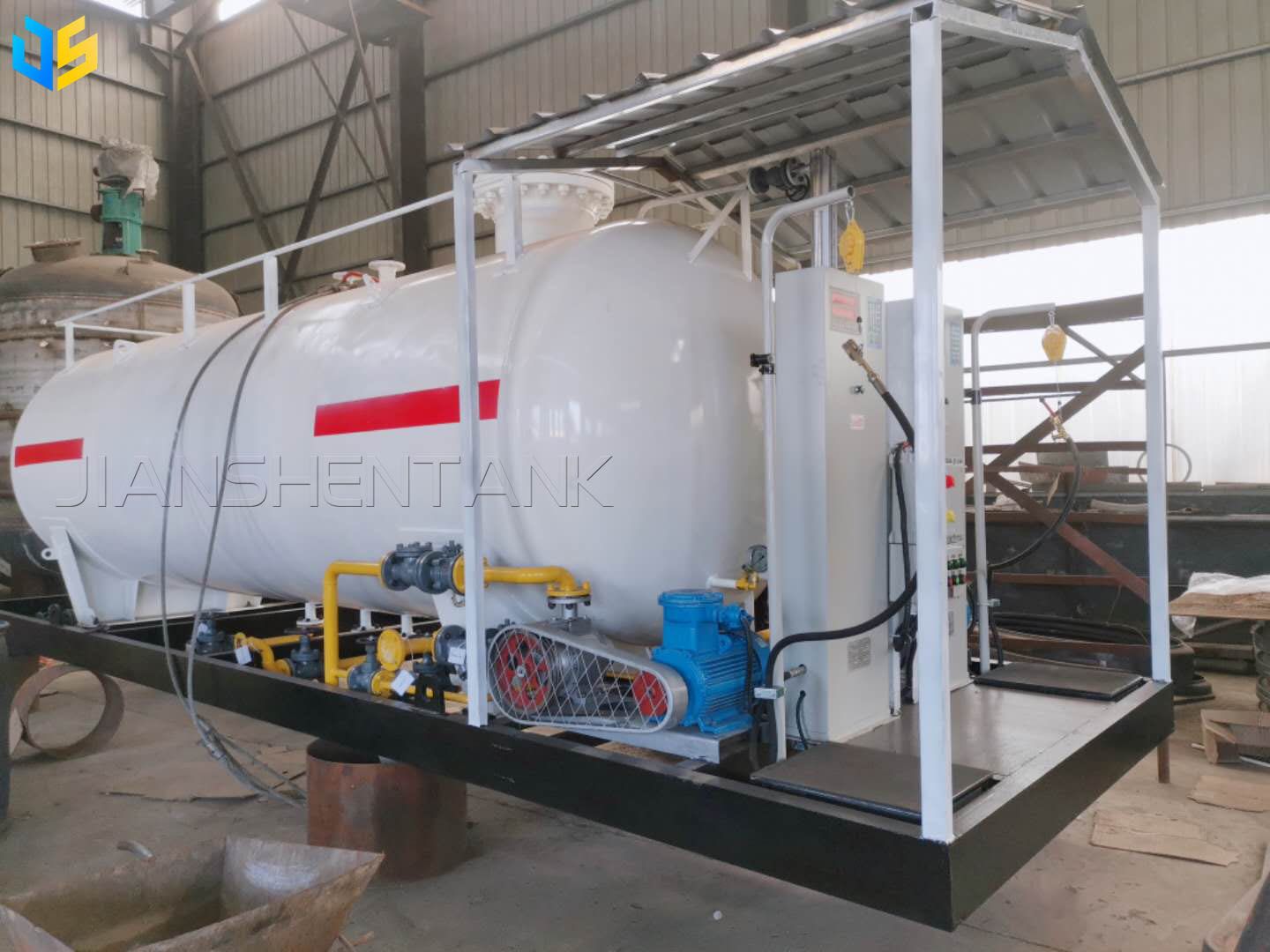
LPG, or liquefied petroleum gas, is a liquid that is formed by compressing and cooling natural gas to low temperatures. CNG, or compressed natural gas, compresses natural gas and stores it in a car’s fuel tank. Compared with traditional gasoline and diesel, they have the following significant advantages:
1. Environmental protection: LPG and CNG produce less waste gas after combustion than traditional fuel, do not produce carbon dioxide and other harmful gases, and have less environmental pollution.
2. Save money: LPG and CNG are about 20% cheaper than gasoline and diesel, and their combustion efficiency is high, which can save fuel costs.
3. High reliability: As automotive fuels, LPG and CNG have low combustion temperatures and are less likely to cause engine knocking. They are also easy to store and refill.